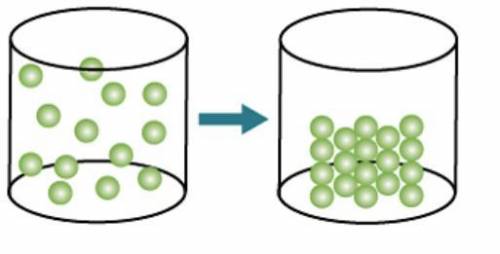
Which change of state is shown in the model?
-condensation
-deposition
-boiling
-...


Answers: 3


Other questions on the subject: Physics

Physics, 23.06.2019 02:30, brodycruce
Afaulty model rocket moves in the xy-plane (the positive y direction is vertically upward). the rocket's acceleration has components ax(t) = ? t2 and ay(t) = ? ? ? t, where ? = 2.50 m/s4 , ? = 9.00 m/s2 , and ? = 1.40 m/s3 . at t = 0 the rocket is at the origin and has velocity ~v0 = v0x ? i + v0y ? j with v0x = 1.00 m/s and v0y = 7.00 m/s. (a) calculate the velocity and position vectors as functions of time. (b) what is the maximum height reached by the rocket? (c) sketch the path of the rocket. (d) what is the horizontal displacement of the rocket when it returns to y = 0?
Answers: 1

Physics, 23.06.2019 06:30, ceceshelby646
Jaylen is a championship runner of the school's track team. during one of his trials, his speed was measured at 15.1 m/s. find jaylen's kinetic energy during that trial if his mass is 54.6 kg.
Answers: 1

Physics, 23.06.2019 10:40, therinzler1825
1. study the scenario. the particles in some system are moving around quickly. a few minutes later, the particles are moving, on average, more slowly. how does this change in motion affect the temperature of the system? the temperature of the system did not change. the speed of the particles does not affect temperature, the number of particles affects the temperature. the temperature of the system is lower now than it was initially. faster moving particles result in a higher temperature for the system. the temperature of the system is higher now than it was initially. slower moving particles result in a higher temperature for the system. the temperature of the system did not change. the speed of the particles has no effect on the temperature, only the type of atom affects the temperature.
Answers: 2

Physics, 23.06.2019 16:00, breannaasmith1122
When a charged balloon sticks to a wall, the downward gravitational force is balanced by an upward static friction force. the normal force is provided by the electrical attraction between the charged balloon and the equal but oppositely charged polarization induced in the wall's molecules. if the mass of a balloon is 1.2 g, its coefficient of static friction with the wall is 0.71, and the average distance between the opposite charges is 0.80 mm, what minimum amount of charge must be placed on the balloon in order for it to stick to the wall? express your answer to two significant figures and include appropriate units.
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Questions in other subjects:



Mathematics, 19.11.2020 22:10



History, 19.11.2020 22:10

English, 19.11.2020 22:10


English, 19.11.2020 22:10