
Physics, 16.10.2020 06:01 sashllely6112
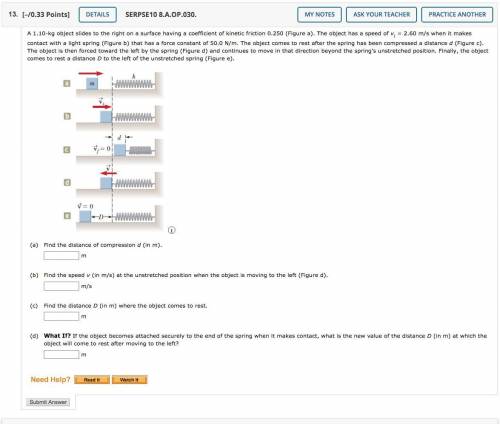
A 1.10-kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.250 (Figure a). The object has a speed of vi = 2.60 m/s when it makes contact with a light spring (Figure b) that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m. The object comes to rest after the spring has been compressed a distance d (Figure c). The object is then forced toward the left by the spring (Figure d) and continues to move in that direction beyond the spring's unstretched position. Finally, the object comes to rest a distance D to the left of the unstretched spring (Figure e).
The right end of a horizontal spring labeled k is attached to a wall. Five images show five configurations as a block labeled m approaches, compresses, and then moves away from the spring.
In figure a, the block is to the left of the spring, and an arrow above the block points to the right.
In figure b, the block is just touching the uncompressed spring, and an arrow labeled vector vi above the block points to the right.
In figure c, the block has compressed the spring by a distance d, and a label indicates vector vf = 0.
In figure d, the block is just touching the uncompressed spring, and an arrow labeled vector v above the block points to the left.
In figure e, the block is a distance D away from the spring, and a label indicates vector v = 0.
(a)
Find the distance of compression d (in m).
m
(b)
Find the speed v (in m/s) at the unstretched position when the object is moving to the left (Figure d).
m/s
(c)
Find the distance D (in m) where the object comes to rest.
m
(d)
What If? If the object becomes attached securely to the end of the spring when it makes contact, what is the new value of the distance D (in m) at which the object will come to rest after moving to the left?
m

Answers: 3


Other questions on the subject: Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 11:00, chaycebell6662
A2.00-m long piano wire with a mass per unit length of 12.0 g/m is under a tension of 8.00 kn. what is the frequency of the fundamental mode of vibration of this wire?
Answers: 3

Physics, 23.06.2019 10:30, sofyan00404
How does the structure of methanol differ from the structure of methane
Answers: 3

Physics, 23.06.2019 20:30, LilBrookilyn2701
Aspacecraft left earth to collect soil samples from mars. which statement is true about the strength of earths gravity on the moving spacecraft? a.) it decreases b.) it increases c.) it remains the same d.) it doesn’t affect the spacecraft
Answers: 1

Physics, 24.06.2019 01:30, almavaldez45
You and your friend peter are putting new shingles on a roof pitched at 20 ∘ . you're sitting on the very top of the roof when peter, who is at the edge of the roof directly below you, 5.1 m away, asks you for the box of nails. rather than carry the 2.0 kg box of nails down to peter, you decide to give the box a push and have it slide down to him.
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
A 1.10-kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.250 (Fi...
Questions in other subjects:


Mathematics, 10.07.2019 09:40



History, 10.07.2019 09:40

History, 10.07.2019 09:40

Mathematics, 10.07.2019 09:40

History, 10.07.2019 09:40


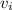 = 2.60 m/s
= 2.60 m/s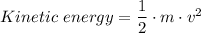
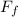 = W × μ
= W × μ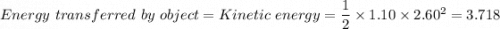
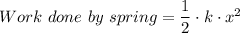
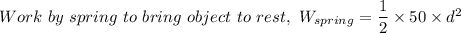
 = 25·d²
= 25·d²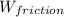 = 1.10×9.81×0.250×d = 2.69775·d
= 1.10×9.81×0.250×d = 2.69775·d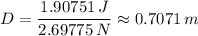
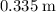 .
.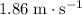 .
.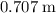 .
.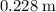 .
.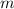 denote the mass of the block. Let
denote the mass of the block. Let 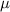 denote the constant of kinetic friction between the object and the surface. Let
denote the constant of kinetic friction between the object and the surface. Let 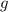 denote the constant of gravitational acceleration.Let
denote the constant of gravitational acceleration.Let 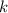 denote the spring constant of this spring.(a)
denote the spring constant of this spring.(a)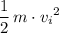 .
.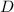 and compressed the spring by the same distance.
and compressed the spring by the same distance. 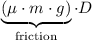 . Elastic potential energy that the spring has gained:
. Elastic potential energy that the spring has gained: 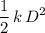 .
.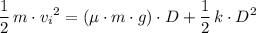 .
.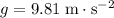 . In the equation above, all symbols other than
. In the equation above, all symbols other than 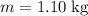 .
.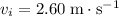 .
.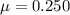 .
.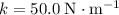 .
.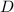 is
is 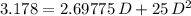 .
.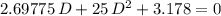 .
.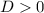 because the energy lost to friction should be greater than zero.
because the energy lost to friction should be greater than zero.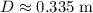 .
.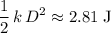 .
.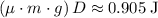 .
.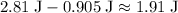 .
.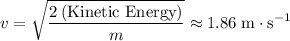 .
.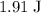 ) would be lost to friction.
) would be lost to friction.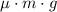 .
.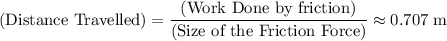 .
.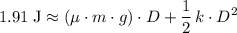 .
.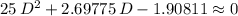 .
.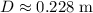 .
. 

