
Physics, 08.07.2020 05:01 heiddy0122
A student sits on a rotating stool holding two 1 kg objects. When his arms are extended horizontally, the objects are 0.9 m from the axis of rotation, and he rotates with angular speed of 0.61 rad/sec. The moment of inertia of the student plus the stool is 6 kg m^2 and is assumed to be constant. The student then pulls the objects horizontally to a radius 0.39 m from the rotation axis.
Required:
a. Calculate the final angular speed of the student. Answer in units of rad/s.
b. Calculate the change in kinetic energy of the system. Answer in units of J.

Answers: 3


Other questions on the subject: Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 00:00, izearaholland7308
What type of nuclear decay causes the atomic number of an element to increase by 1?
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 09:00, winterblanco
The pressure proportional to the area a- inversely b- directly c- increase d-decrease
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 09:10, kingdesto3481
Which lists the organs in the correct order as food passes from the mouth to anus?
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 11:00, vanvalenpeyt
The star betelgeuse is about 600 light-years away. if it explodes tonight, a. we'll know because debris from the explosion will rain down on us from space. b. we'll know it immediately because it will be brighter than the full moon in the sky. c. we won't know about it until 600 years from now. d. none of the above.
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
A student sits on a rotating stool holding two 1 kg objects. When his arms are extended horizontally...
Questions in other subjects:



Mathematics, 30.05.2020 05:04




Mathematics, 30.05.2020 05:04


Mathematics, 30.05.2020 05:04

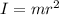 = 2 x
= 2 x 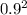 = 1.62 kg-m^2
= 1.62 kg-m^2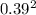 = 0.304 kg-m^2
= 0.304 kg-m^2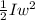
 =
= 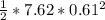 = 1.417 J
= 1.417 J = 1.717 J
= 1.717 J

