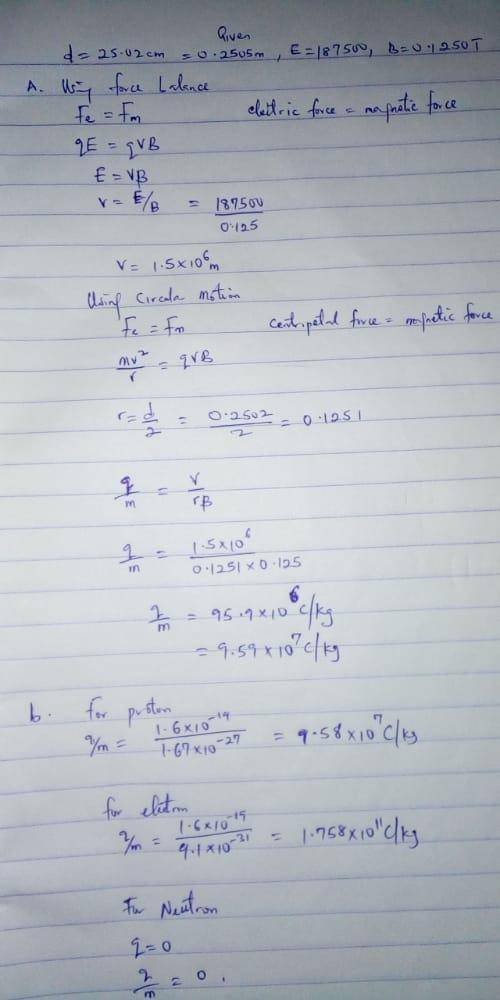1. An unknown charged particle passes without deflection through crossed electric and magnetic fields of strengths 187,500 V/m and 0.1250 T, respectively. The particle passes out of the electric field, but the magnetic field continues, and the particle makes a semicircle of diameter 25.05 cm.
Part A. What is the particle's charge-to-mass ratio?
Part B. Can you identify the particle?
a. can't identify
b. proton
c. electron
d. neutron
2. A neutral lithium atom has three electrons. Two of these electrons form an "inner core," but the third-the valence electron-orbits at a much larger radius. From the valence electron's perspective, it is orbiting a spherical ball of charge having net charge +1e (i. e., the three protons in the nucleus and the two inner-core electrons). The energy required to ionize a lithium atom is 5.14 eV. Hint: Consider the energy needed to remove the electron and the force needed to give the electron a circular orbit.
Part A. According to Rutherford's nuclear model of the atom, what is the orbital radius of the valence electron? Express your answer with the appropriate units.
Part B. According to Rutherford's nuclear model of the atom, what is the speed of the valence electron? Express your answer with the appropriate units.

Answers: 1


Other questions on the subject: Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 04:00, katieleeisaacs8368
Ametal ball with a mass of 0.028 kg is dropped from rest at a height of 1.0 meters above the ground. assuming the energy in the ball is conserved, how much kinetic energy will the ball have when it is 0.5 meters above the ground?
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 05:00, anondriap
Which statements describe the movement of ocean currents around the globe? check all that apply. strong winds force warm water to sink to the ocean floor. the coriolis effect causes warm and cold water to mix. cool dense water sinks to the ocean floor. warm water replaces cool surface water. wind blowing parallel to the shore causes upwelling of cool water.
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 09:00, winterblanco
The pressure proportional to the area a- inversely b- directly c- increase d-decrease
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 11:10, cmflores3245
While standing outdoors one evening, you are exposed to the following four types of electromagnetic radiation: yellow light from a sodium street lamp, radio waves from an am radio station, radio waves from an fm radio station, and microwaves from an antenna of a communications system. rank these type of waves in terms of increasing photon energy.
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
1. An unknown charged particle passes without deflection through crossed electric and magnetic field...
Questions in other subjects:

Mathematics, 01.02.2021 23:10

Chemistry, 01.02.2021 23:10

Chemistry, 01.02.2021 23:10


Computers and Technology, 01.02.2021 23:10

Mathematics, 01.02.2021 23:10



Physics, 01.02.2021 23:10