Physics, 25.03.2020 02:50 jadeaguayo28
Suppose our experimenter repeats his experiment on a planet more massive than Earth, where the acceleration due to gravity is g = 30 m/s². When he releases the ball from chin height without giving it a push, how will the ball's behavior differ from its behavior on Earth? Ignore friction and air resistance.
(Select all that apply.)
a. It will take more time to return to the point from which it was released.
b. It will smash his face.
c. Its mass will be greater.
d. It will take less time to return to the point from which it was released.
e. It will stop well short of his face.

Answers: 1


Other questions on the subject: Physics



Physics, 22.06.2019 16:40, jcblake
Beryl states that insulation with the smallest possible thermal conductivity is best to keep a house warm in winter, but worst for keeping a house cool in summer. sapphire insists the reverse is true: low thermal conductivity is good in the summer, but bad in the winter. which one, if either is correct? a. beryl, because low thermal conductivity results in low heat transfer. b. beryl, because low thermal conductivity results in high heat transfer. d. sapphire, because low thermal conductivity results in high heat transfer. e. neither, because low heat transfer is desirable both in summer and in winter.
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 17:00, griffinkiley22
Two manned satellites approaching one another at a relative speed of 0.550 m/s intend to dock. the first has a mass of 2.50 ✕ 103 kg, and the second a mass of 7.50 ✕ 103 kg. assume that the positive direction is directed from the second satellite towards the first satellite. (a) calculate the final velocity after docking, in the frame of reference in which the first satellite was originally at rest.(b) what is the loss of kinetic energy in this inelastic collision? (c) repeat both parts, in the frame of reference in which the second satellite was originally at rest. final velocity(d) loss of kinetic energy = ?
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
Suppose our experimenter repeats his experiment on a planet more massive than Earth, where the accel...
Questions in other subjects:


History, 24.06.2019 21:00

Health, 24.06.2019 21:00



Biology, 24.06.2019 21:00


Mathematics, 24.06.2019 21:00


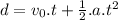 , where:
, where: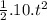
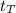 =
= 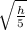
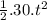
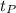 =
= 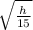
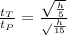
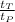 =
= 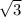 or
or