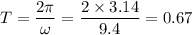A mass free to vibrate on a level, frictionless surface at the end of a horizontal spring is pulled 35 cm from its equilibrium position and released. At an instant 0.12 s later, its displacement has decreased to 15 cm, without the mass having passed through equilibrium. Calculate the period. ( 0.67 s).

Answers: 3


Other questions on the subject: Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 20:20, jazmaine1217
When many atoms are split in a chain reaction, a large explosion occurs. this is an example of what type of energy conservation
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 14:00, mariahgriego4126
Why is rain likely when warm, moisture-laden air meets cold air? a) the lighter warm air will rise and cool down, causing condensation and rain. b) the cold air moves faster and pushes the warm air away, causing condensation and rain. c) the moisture in the warm air condenses on contact with the cold air, causing rain to fall. d) the cold air mixes with the warm air, reducing its temperature causing moisture to condense.
Answers: 1

You know the right answer?
A mass free to vibrate on a level, frictionless surface at the end of a horizontal spring is pulled...
Questions in other subjects:



Medicine, 09.10.2019 01:00







 , of an SHM is given by
, of an SHM is given by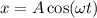
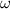 is the angular frequency.
is the angular frequency.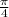 radian.
radian.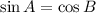 if A and B are complementary.
if A and B are complementary.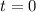 ,
, 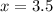
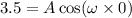
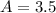
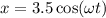
 ,
, 
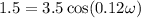
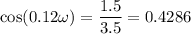
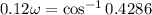
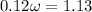
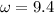
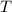 , is related to
, is related to