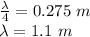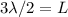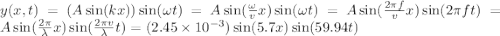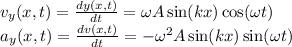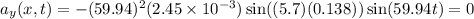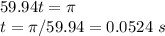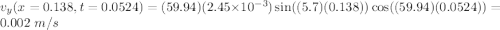Physics, 03.01.2020 00:31 ester32152
In lab, your instructor generates a standing wave using a thin string of length l = 1.65 m fixed at both ends. you are told that the standing wave is produced by the superposition of traveling and reflected waves, where the incident traveling waves propagate in the +x direction with an amplitude a = 2.45 mm and a speed vx = 10.5 m/s . the first antinode of the standing wave is a distance of x = 27.5 cm from the left end of the string, while a light bead is placed a distance of 13.8 cm to the right of the first antinode. what is the maximum transverse speed vy of the bead? make sure to use consistent distance units in your calculations.
given that the distance from the left end of the string to the first antinode is 27.5 cm , calculate the wavelength of the standing wave on the string. remember to convert all measurements into units of meters before performing this calculation.

Answers: 1


Other questions on the subject: Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 08:30, bollipard1183
Brutus, the dog, is pulling a bone to the left with a force of 20 n. lassie, another dog, is pulling a bone to the right with a force of 18n. what is the net force? a. b. c.
Answers: 1


Physics, 22.06.2019 19:30, u8p4
Water is siphoned from a large tank and discharges into the atmosphere through a 50-mm diameter tube. the end of the tube is b = 2.6 m below the tank bottom which is a = 6.7 m deep, and viscous effects are negligible. determine the maximum height h over which the water can be siphoned without cavitation occurring. atmospheric pressure is 101.4 kpa, and the water vapor pressure is 1.79 kpa (absolute). report your answer in meters to two decimal places.
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 19:40, cordovatierra16
Two charged particles, q1 and q2, are located on the x-axis, with q1 at the origin and q2 initially at x1 = 12.2 mm. in this configuration, q1 exerts a repulsive force of 2.62 µn on q2. particle q2 is then moved to x2 = 18.0 mm. what is the force (magnitude and direction) that q2 exerts on q1 at this new location? (give the magnitude in µn.)
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
In lab, your instructor generates a standing wave using a thin string of length l = 1.65 m fixed at...
Questions in other subjects:

Mathematics, 14.11.2020 04:40



Mathematics, 14.11.2020 04:40


History, 14.11.2020 04:40


English, 14.11.2020 04:40

Mathematics, 14.11.2020 04:40