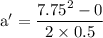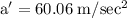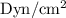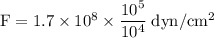Physics, 22.11.2019 21:31 chaparoonie15
While unrealistic, we will examine the forces on a leg when one falls from a height by approximating the leg as a uniform cylinder of bone with a diameter of 2.3 cm and ignoring any shear forces. human bone can be compressed with approximately 1.7 × 108 n/m2 before breaking. a man with a mass of 80 kg falls from a height of 3 m. assume his acceleration once he hits the ground is constant. for these calculations, g = 10 m/s2.
part a: what is his speed just before he hits the ground?
part b: with how much force can the "leg" be compressed before breaking?
part c: if he lands "stiff legged" and his shoes only compress 1 cm, what is the magnitude of the average force he experiences as he slows to a rest?
part d: if he bends his legs as he lands, he can increase the distance over which he slows down to 50 cm. what would be the average force he experiences in this scenario?
part e: dyne is also a unit of force and 1 dyn= 10−5 n. what is the maximum a bone can be compressed in dyn/cm2?
part f: which of the following is the reason that we would recommend that the man bend his legs while landing from such a fall?
a. bending his legs allows him to push back up on the ground and negate some of the effects of the force applied by the ground.
b. bending his legs decreases the speed at which he hits the ground, thus decreasing the force applied by the ground.
c. bending his legs decreases his overall change in momentum, thus decreasing the force applied by the ground.
d. bending his legs increases the time over which the ground applies force, thus decreasing the force applied by the ground.

Answers: 3


Other questions on the subject: Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 11:00, stankyweezle
A0.580-kg rock is tied to the end of a string and is swung in a circle with a radius of 0.500 meters. the velocity of the rock is 4.50 m/s. what is the centripetal force acting on the rock? 15.5 n 5.22 n 69.8 n 23.5 n
Answers: 3

Physics, 22.06.2019 13:00, help1572
Aplayground merry-go-round has a radius of 4.6 m and a moment of inertia of 200 kg-m2 and turns with negligible friction about a vertical axle through its center. a child applies a 26.0 n force tangentially to the edge of the merry-go-round for 15.0 seconds. if the merry-go-round is initially at rest, how much work did the child do on the merry-go-round?
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 14:20, jeny89
4r-134a enters the condenser of a residential heat pump at 800 kpa and 50°c at a rate of 0.022 kg/s and leaves at 750 kpa subcooled by 3°c. the refrigerant enters the compressor at 200 kpa superheated by 4°c determine (a) the isentropic efficiency of the compressor, (b) the rate of heat supplied to the heated room, and (c) the cop of the heat pump. also, determine (d) the cop and rate of heat supplied to the heated room if this heat pump operated on the ideal vapor-compression cycle between the pressure limits of 200 and 800 kpa. (0.757, 4.37 kw, 5.12, 6.18, 3.91 kw)
Answers: 3

Physics, 22.06.2019 15:30, anonymous1813
What is the increase in density of a medium due to wave travel?
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
While unrealistic, we will examine the forces on a leg when one falls from a height by approximating...
Questions in other subjects:







Mathematics, 01.07.2020 15:01


Physics, 01.07.2020 15:01

Mathematics, 01.07.2020 15:01

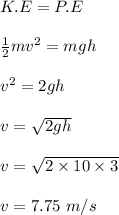
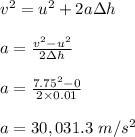
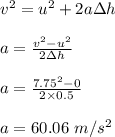
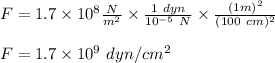
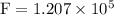 N
N
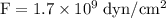

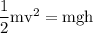
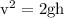

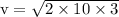
 ---- (1)
---- (1)
 in equation (1),
in equation (1),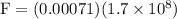
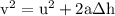 ---- (2)
---- (2)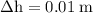 .
.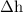 in equation (2),
in equation (2),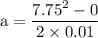
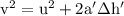 ---- (3)
---- (3) .
. in equation (3),
in equation (3),