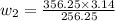Physics, 07.09.2019 16:10 nessuhbae6731
A25 kg child stands 2.5 m from the center of a frictionless merry‐go‐round, which has a 200 kg*m^2 moment of inertia and is spinning with one revolution every two seconds. the child then moves inward to a radius of 1.5 m. a) what is the initial angular velocity of the merry‐go‐round?
b) what is the new angular velocity of the merry‐go‐round, after the child moves?
c) by how much did the kinetic energy of the merry‐go‐round increase? where did this energy come from?

Answers: 3


Other questions on the subject: Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 04:00, louiecampos
Determine the maximum r-value of the polar equation r =3+3 cos 0
Answers: 1


Physics, 22.06.2019 15:30, lexiepedit4958
The movement of electrons between atoms is called an
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
A25 kg child stands 2.5 m from the center of a frictionless merry‐go‐round, which has a 200 kg*m^2 m...
Questions in other subjects:


Geography, 15.12.2021 21:50


Biology, 15.12.2021 21:50



Mathematics, 15.12.2021 21:50