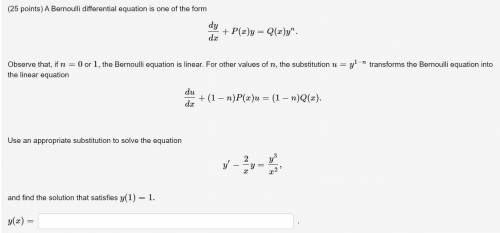
A Bernoulli differential equation is one of the form
dy/dx+P(x)y=Q(x)y^n.
Observe that...

Mathematics, 26.10.2021 18:10 realpcy7515
A Bernoulli differential equation is one of the form
dy/dx+P(x)y=Q(x)y^n.
Observe that, if n=0 or 1, the Bernoulli equation is linear. For other values of n, the substitution u=y^(1−n) transforms the Bernoulli equation into the linear equation
du/dx+(1−n)P(x)u=(1−n)Q(x).
Use an appropriate substitution to solve the equation
y′−(2/x)y=y^3/x^2,
and find the solution that satisfies y(1)=1.
y(x)=

Answers: 2


Other questions on the subject: Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:10, Calvinailove13
Pls! does anybody know a shortcut for answering these types of questions in the future?
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 01:00, ryantrajean7
The collection of beautiful oil paintings currently on display at an art gallery well defined; set not well defined; not a set
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 02:00, hello123485
Find a third-degree polynomial equation with rational coefficients that has roots -2 and 6+i
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 02:40, torybobadilla
Explain how the quotient of powers was used to simplify this expression.
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Questions in other subjects:












