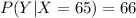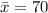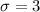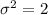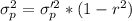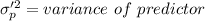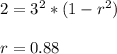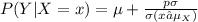Mathematics, 22.07.2021 20:20 colton7856
The scores from the first test for students in my statistics class have an average of 70 and a standard deviation of 3. The scores from the second test has the same average and standard deviation as scores from the first test. The variance of the score from the second test given that the score in the first test is 65, is 2. Assume the scores of the students in the first test and second test are positively correlated and have a bivariate normal distribution. Calculate the average scores of the students in the second test given that the scores in the first test are 65.

Answers: 3


Other questions on the subject: Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 17:00, SillyEve
In tossing one coin 10 times, what are your chances for tossing a head? a tail? 2. in tossing one coin 100 times, what are your chances for tossing a head? a tail? 3. in tossing one coin 200 times, what are your chances for tossing a head? a tail? deviation = ((absolute value of the difference between expected heads and observed heads) + (absolute value of the difference between expected tails and observed tails)) divided by total number of tosses. this value should always be positive. 4. what is the deviation for 10 tosses? 5. what is the deviation for the 100 tosses? 6. what is the deviation for 200 tosses? 7. how does increasing the total number of coin tosses from 10 to 100 affect the deviation? 8. how does increasing the total number of tosses from 100 to 200 affect the deviation? 9. what two important probability principles were established in this exercise? 10. the percent of occurrence is the obtained results divided by the total tosses and multiplied by 100%. toss the coins 100 times and record your results. calculate the percent occurrence for each combination. percent head-head occurrence: percent tail-tail occurrence: percent head-tail occurrence:
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:30, 128585
Adoctor administers a drug to a 38-kg patient, using a dosage formula of 50 mg/kg/day. assume that the drug is available in a 100 mg per 5 ml suspension or in 500 mg tablets. a. how many tablets should a 38-kg patient take every four hours? b. the suspension with a drop factor of 10 ggt/ml delivers the drug intravenously to the patient over a twelve-hour period. what flow rate should be used in units of ggt/hr? a. the patient should take nothing pills every four hours. (type an integer or decimal rounded to the nearest hundredth as needed.)
Answers: 1

You know the right answer?
The scores from the first test for students in my statistics class have an average of 70 and a stand...
Questions in other subjects:



Mathematics, 13.01.2021 21:50




History, 13.01.2021 21:50

Computers and Technology, 13.01.2021 21:50