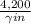Chemistry, 10.03.2020 09:06 22savage2017
In the red blood cell, glucose is transported into the cell against its concentration gradient.
The energy for this transport is supplied by the hydrolysis of ATP:
ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi at 298K
Assume the overall transport reaction is:
ATP + H2O + 2glucose(out) → ADP + Pi + 2glucose(in).
(a) At 37 °C, under conditions where [ATP], [ADP], and [Pi] are each held constant at 100 mM by cell metabolism, what is the maximum value of [glucose(in)]/[glucose(out)]? You can assume the activity coefficients of all species are 1.
(b) In an actual cell, the glucose inside the cell may exhibit non-ideal behavior. How would this affect the activity coefficient? Would this increase or decrease the maximum concentration gradient obtainable?

Answers: 3


Other questions on the subject: Chemistry


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 06:00, applejulianamoreno
If a polyatomic ionic compound has gained two hydrogen ions, then how does its name begin?
Answers: 3


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 16:50, struckedblazing
Answer asap need it by wednesday morning calculate the ph of 0.02m hcl best answer will be brainliest
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
In the red blood cell, glucose is transported into the cell against its concentration gradient.
Questions in other subjects:






Mathematics, 27.04.2021 02:00


Computers and Technology, 27.04.2021 02:00


![\frac{[glucose(in)]}{[glucose_{(out)}]}](/tpl/images/0540/7312/e1a96.png) = 4,200
= 4,200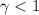 , we conclude that the
, we conclude that the 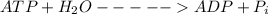
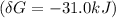
![\delta G = \delta G^0 +RTIn \frac{[ADP][P_i]}{[ATP]}](/tpl/images/0540/7312/ca0ac.png)
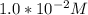
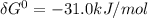
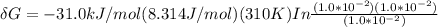
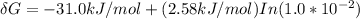
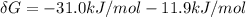
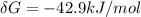
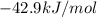 is the energy available for the transport of glucose.
is the energy available for the transport of glucose.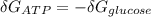
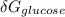
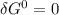 (since no energy input at equilibrium)
(since no energy input at equilibrium)![\delta G = \delta G^0 + RT In \frac{[glucose(in)]^2}{[glucose_{(out)}]^2}](/tpl/images/0540/7312/fa3f3.png)

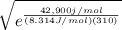
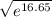
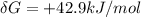
![0+RT In \frac{[glucose (in)] \gamma^2 in}{[glucose{(out)}]^2}](/tpl/images/0540/7312/ef0ae.png)
![\frac{[glucose(in)] \gamma^2 in}{[glucose_{(out)}]}](/tpl/images/0540/7312/8a13f.png) =
=