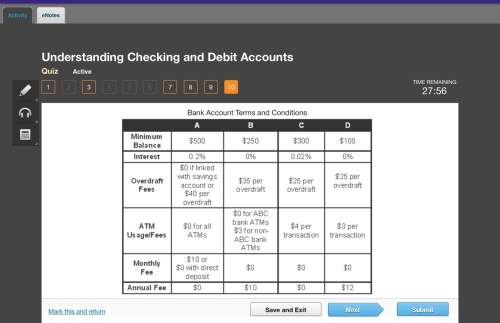
Activity-Based Product Costing
Sweet Sugar Company manufactures three products (white sugar, brown sugar, and powdered sugar) in a continuous production process. Senior management has asked the controller to conduct an activity-based costing study. The controller identified the amount of factory overhead required by the critical activities of the organization as follows:
Activity Budgeted Activity Cost
Production $471,200
Setup 310,800
Inspection 81,000
Shipping 156,000
Customer service 65,500
Total $1,084,500
The activity bases identified for each activity are as follows:
Activity Activity Base
Production Machine hours
Setup Number of setups
Inspection Number of inspections
Shipping Number of customer orders
Customer service Number of customer service requests
The activity-base usage quantities and units produced for the three products were determined from corporate records and are as follows:
Machine Hours Number of
Setups Number of
Inspections Number of
Customer Orders Customer
Service
Requests Units
White sugar 3,340 180 200 780 50 8,350
Brown sugar 2,130 270 300 2,150 320 5,325
Powdered sugar 2,130 250 500 970 130 5,325
Total 7,600 700 1,000 3,900 500 19,000
Each product requires 0.9 machine hour per unit.
Required:
If required, round all per unit amounts to the nearest cent.
1. Determine the activity rate for each activity.
Production $ per machine hour
Setup $ per setup
Inspection $ per move
Shipping $ per cust. ord.
Customer service $ per customer service request
2. Determine the total and per-unit activity cost for all three products.
Total Activity Cost Activity Cost Per Unit
White sugar $ $
Brown sugar
Powdered sugar
3. Why aren’t the activity unit costs equal across all three products since they require the same machine time per unit?
The unit costs are different because the products consume many activities in ratios different from the .

Answers: 2


Other questions on the subject: Business

Business, 21.06.2019 17:10, jasonweber8718
Teller co. is planning to sell 900 boxes of ceramic tile, with production estimated at 870 boxes during may. each box of tile requires 44 pounds of clay mix and a quarter hour of direct labor. clay mix costs $0.40 per pound and employees of the company are paid $12.00 per hour. manufacturing overhead is applied at a rate of 110% of direct labor costs. teller has 3,900 pounds of clay mix in beginning inventory and wants to have 4,500 pounds in ending inventory. what is the total amount to be budgeted for manufacturing overhead for the month?
Answers: 1

Business, 21.06.2019 22:40, gobertbrianna40
Job a3b was ordered by a customer on september 25. during the month of september, jaycee corporation requisitioned $2,400 of direct materials and used $3,900 of direct labor. the job was not finished by the end of the month, but needed an additional $2,900 of direct materials in october and additional direct labor of $6,400 to finish the job. the company applies overhead at the end of each month at a rate of 100% of the direct labor cost. what is the amount of job costs added to work in process inventory during october?
Answers: 3

Business, 22.06.2019 00:00, leilakainani26
Alandlord rented an art studio to an artist. under the terms of the signed, written, two-year lease, the artist agreed to pay the landlord $1,000 per month and to assume responsibility for all necessary repairs. after the first year of the lease, the artist assigned the balance of his lease to a sculptor. the landlord approved the sculptor as a tenant and accepted two rent payments from her, and then the landlord sold the building to an investor. the sculptor had made two payments to the investor when an electrical fire broke out in the studio, injuring the sculptor. the fire was caused by faulty wiring. the landlord was aware that there was a dangerous wiring problem when he leased the property to the artist. but when the landlord discovered how costly repairs would be, he decided it would be more profitable to sell the property than to repair it. the problem was not easily discoverable by anyone other than an expert electrician, and the landlord did not tell the artist, the sculptor, or the investor about the problem. the sculptor sues to recover damages for her injuries. from whom can the sculptor recover?
Answers: 3

Business, 22.06.2019 04:30, mt137896
Required prepare the necessary adjusting entries in the general journal as of december 31, assuming the following: on september 1, the company entered into a prepaid equipment maintenance contract. birch company paid $3,400 to cover maintenance service for six months, beginning september 1. the payment was debited to prepaid maintenance. supplies on hand at december 31 are $3,900. unearned commission fees at december 31 are $7,000. commission fees earned but not yet billed at december 31 are $3,500. (note: debit fees receivable.) birch company's lease calls for rent of $1,600 per month payable on the first of each month, plus an annual amount equal to 1% of annual commissions earned. this additional rent is payable on january 10 of the following year. (note: be sure to use the adjusted amount of commissions earned in computing the additional rent.)
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Activity-Based Product Costing
Sweet Sugar Company manufactures three products (white sugar, brown...
Questions in other subjects:


History, 16.10.2019 13:50


English, 16.10.2019 13:50


Mathematics, 16.10.2019 13:50


Mathematics, 16.10.2019 13:50


Geography, 16.10.2019 13:50