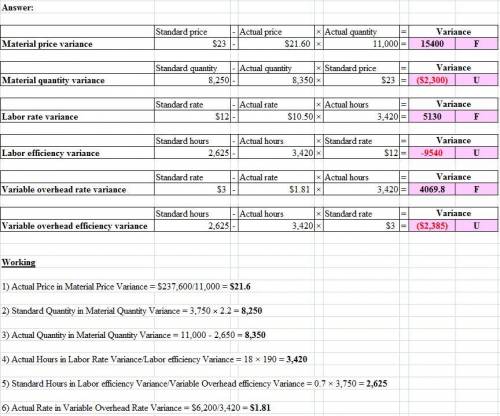
Becton Labs, Inc., produces various chemical compounds for industrial use. One compound, called Fludex, is prepared using an elaborate distilling process. The company has developed standard costs for one unit of Fludex, as follows:
Standard Quantity Standard Price
or Rate Standard Cost
Direct materials 2.00 ounces $ 30.00 per ounce $ 60.00
Direct labor 0.50 hours $ 14.00 per hour 7.00
Variable manufacturing overhead 0.50 hours $ 3.40 per hour 1.70
$ 68.70
During November, the following activity was recorded relative to production of Fludex:
a. Materials purchased, 10,000 ounces at a cost of $287,000.
b.
There was no beginning inventory of materials; however, at the end of the month, 3,000 ounces of material remained in ending inventory.
c.
The company employs 20 lab technicians to work on the production of Fludex. During November, they worked an average of 130 hours at an average rate of $12.00 per hour.
d.
Variable manufacturing overhead is assigned to Fludex on the basis of direct labor-hours. Variable manufacturing overhead costs during November totaled $4,700.
e. During November, 3,400 good units of Fludex were produced .
Required:
1. For direct materials:
a.
Compute the price and quantity variances. (Input all amounts as positive values. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i. e, zero variance).)
b. The materials were purchased from a new supplier who is anxious to enter into a long-term purchase contract. Would you recommend that the company sign the contract?
Yes
No
2. For direct labor:
a.
Compute the rate and efficiency variances. (Input all amounts as positive values. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i. e, zero variance).)
b.
In the past, the 20 technicians employed in the production of Fludex consisted of 4 senior technicians and 16 assistants. During November, the company experimented with fewer senior technicians and more assistants in order to save costs. Would you recommend that the new labor mix be continued?
Yes
No
3.
Compute the variable overhead rate and efficiency variances. (Input all amounts as positive values. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i. e, zero variance).)

Answers: 2


Other questions on the subject: Business

Business, 22.06.2019 13:50, xcoder1732
Suppose portugal has 700 workers and 26,000 units of capital, and france has 18,000 workers and 700 units of capital. technology is identical in both countries. assume that wine is the capital-intensive good and cloth is the labor-intensive good. which of the following statements is correct if the nations start trading with each other? a) wages will increase in portugal. b) rental rates in france will increase. c) wages in france will decrease. d) rental rates in portugal will increase.
Answers: 2

Business, 22.06.2019 23:40, coreycbg1127
Joint cost cheyenne, inc. produces three products from a common input. the joint costs for a typical quarter follow: direct materials $45,000 direct labor 55,000 overhead 60,000 the revenues from each product are as follows: product a $75,000 product b 80,000 product c 30,000 management is considering processing product a beyond the split-off point, which would increase the sales value of product a to $116,000. however, to process product a further means that the company must rent some special equipment costing $17,500 per quarter. additional materials and labor also needed would cost $12,650 per quarter. a. what is the gross profit currently being earned by the three products for one quarter? $answer b. what is the effect on quarterly profits if the company decides to process product a further? $answer
Answers: 2


Business, 23.06.2019 00:00, silonis21
1. consider a two-firm industry. firm 1 (the incumbent) chooses a level of output qı. firm 2 (the potential entrant) observes qı and then chooses its level of output q2. the demand for the product is p 100 q, where q is the total output sold by the two firms which equals qi +q2. assume that the marginal cost of each firm is zero. a) find the subgame perfect equilibrium levels of qi and q2 keeping in mind that firm 1 chooses qi first and firm 2 observes qi and chooses its q2. find the profits of the two firms-n1 and t2- in the subgame perfect equilibrium. how do these numbers differ from the cournot equilibrium? b) for what level of qi would firm 2 be deterred from entering? would a rational firm 1 have an incentive to choose this level of qi? which entry condition does this market have: blockaded, deterred, or accommodated? now suppose that firm 2 has to incur a fixed cost of entry, f> 0. c) for what values of f will entry be blockaded? d) find out the entry deterring level of q, denoted by q1', a expression for firm l's profit, when entry is deterred, as a function of f. for what values of f would firm 1 use an entry deterring strategy?
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Becton Labs, Inc., produces various chemical compounds for industrial use. One compound, called Flud...
Questions in other subjects:

English, 28.07.2019 04:34

Health, 28.07.2019 04:34

Mathematics, 28.07.2019 04:34


Chemistry, 28.07.2019 04:34

Computers and Technology, 28.07.2019 04:34