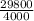Sweeten company had no jobs in progress at the beginning of march and no beginning inventories. the company has two manufacturing departments--molding and fabrication. it started, completed, and sold only two jobs during march - job p and job q. the following additional information is available for the company as a whole and for jobs p and q (all data and questions relate to the month of march): molding fabrication total estimated total machine-hours used 2,500 1,500 4,000 estimated total fixed manufacturing overhead $ 13,000 $ 16,800 $ 29,800 estimated variable manufacturing overhead per machine-hour $ 2.60 $ 3.40 job p job q direct materials $ 25,000 $ 14,000 direct labor cost $ 30,600 $ 12,300 actual machine-hours used: molding 2,900 2,000 fabrication 1,800 2,100 total 4,700 4,100 sweeten company had no underapplied or overapplied manufacturing overhead costs during the month. required: for questions 1-8, assume that sweeten company uses a plantwide predetermined overhead rate with machine-hours as the allocation base. for questions 9-15, assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both departments. 1. what was the company’s plantwide predetermined overhead rate? 2. how much manufacturing overhead was applied to job p and how much was applied to job q? 3. what was the total manufacturing cost assigned to job p? 4. if job p included 20 units, what was its unit product cost? 5. what was the total manufacturing cost assigned to job q? 6. if job q included 30 units, what was its unit product cost? 7. assume that sweeten company used cost-plus pricing (and a markup percentage of 80% of total manufacturing cost) to establish selling for all of its jobs. what selling price would company have established for jobs p and q? what are the selling prices for both jobs when stated on a per unit basis? 8. what was sweeten company’s cost of goods sold for march? 9. what were the company’s predetermined overhead rates in the molding department and the fabrication department? 10. how much manufacturing overhead was applied from the molding department to job p and how much was applied to job q? 11. how much manufacturing overhead was applied from the fabrication department to job p and how much was applied to job q? 12. if job p included 20 units, what was its unit product cost? 13. if job q included 30 units, what was its unit product cost? 14. assume that sweeten company used cost-plus pricing (and a markup percentage of 80% of total manufacturing cost) to establish selling prices for all of its jobs. what selling price would the company have established for jobs p and q? what are the selling prices for both jobs when stated on a per unit basis? 15. what was sweeten company’s cost of goods sold for march?

Answers: 1


Other questions on the subject: Business

Business, 22.06.2019 03:30, jadahilbun01
Instructions: use the following information to construct the 2000 balance sheet and income statement for carolina business machines. round all numbers to the nearest whole dollar. all numbers are in thousands of dollars. be sure to read the whole problem before you jump in and get started. at the end of 1999 the firm had $43,000 in gross fixed assets. in 2000 they purchased an additional $14,000 of fixed asset equipment. accumulated depreciation at the end of 1999 was $21,000. the depreciation expense in 2000 is $4,620. at the end of 2000 the firm had $3,000 in cash and $3,000 in accounts payable. in 2000 the firm extended a total of $9,000 in credit to a number of their customers in the form of accounts receivable. the firm generated $60,000 in sales revenue in 2000. their cost of goods sold was 60 percent of sales. they also incurred salaries and wages expense of $10,000. to date the firm has $1,000 in accrued salaries and wages. they borrowed $10,000 from their local bank to finance the $15,000 in inventory they now have on hand. the firm also has $7,120 invested in marketable securities. the firm currently has $20,000 in long-term debt outstanding and paid $2,000 in interest on their outstanding debt. over the firm's life, shareholders have put up $30,000. eighty percent of the shareholder's funds are in the form of retained earnings. the par value per share of carolina business machines stock is
Answers: 3

Business, 22.06.2019 08:30, hartzpeyton136
Match each item to check for while reconciling a bank account with the document to which it relates.(there's not just one answer)1. balancing account statement2. balancing check registera. nsf feesb. deposits in transitc. interest earnedd. bank errors
Answers: 2

Business, 22.06.2019 11:10, amunson40
The green fiddle has declared a $5 per share dividend. suppose capital gains are not taxed, but dividends are taxed at 15 percent. new irs regulations require that taxes be withheld at the time the dividend is paid. green fiddle stock sells for $71.50 per share, and the stock is about to go ex-dividend. what will the ex-dividend price be?
Answers: 2

Business, 22.06.2019 12:30, victorialeona81
Provide an example of open-ended credit account that caroline has. caroline blue's credit report worksheet.
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Sweeten company had no jobs in progress at the beginning of march and no beginning inventories. the...
Questions in other subjects:





Mathematics, 27.01.2021 22:00



Arts, 27.01.2021 22:00

Mathematics, 27.01.2021 22:00

Mathematics, 27.01.2021 22:00