
Biology, 11.06.2020 21:57 monyeemonyee12
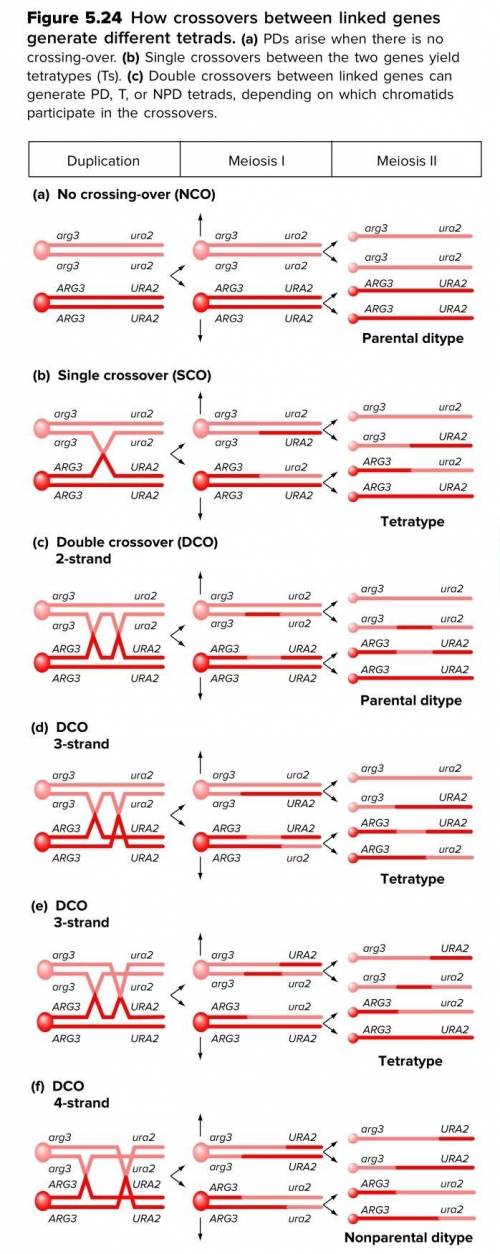
This problem leads you through the derivation of a corrected equation for RF in yeast tetrad analysis that takes into account double crossover (DCO) meioses. A yeast strain that cannot grow in the absence of the amino acid histidine (his−) is mated with a yeast strain that cannot grow in the absence of the amino acid lysine (lys−). Among the 400 unordered tetrads resulting from this mating, 233 were PD, 11 were NPD, and 156 were T.
a. What types of spores are in the PD, NPD, and T tetrads?
b. Are the his and lys genes linked? How do you know?
c. Using the simple equation RF = 100 × [NPD +(1/2)T]/total tetrads, calculate the distance in mapunits between the his and lys genes.
d. If you think about all the kinds of meiotic eventsthat could occur (refer to Fig. 5.24), you can see that the calculation you did in part (c) may substantially underestimate RF. What kinds of meioses (NCO, SCO, or DCO) generated each of the tetrad types in this cross?
e. What incorrect assumptions does the simple RFequation you used in part (c) make about themeiotic events producing each type of tetrad? Whencould these assumptions nevertheless be correct?
f. Use your answers to part (d) to determine thenumber of NCO, SCO, and DCO meioses thatgenerated the 400 tetrads.
g. Use your answers to part (f) to write a generalequation that relates the number of DCO meiosesto the number of the various tetrad types. Thenwrite another general equation that computes thenumber of SCO meioses as a function of the number of the various tetrad types.
h. Based on your answer to part (f), calculate theaverage number of crossovers per meiosis (m)between his and lys.
i. Use your answer to (h) to write an equation for min terms of NCO, SCO, and DCO meioses.
j. What is the relationship between RF and m?
k. Use your answer to part (j) to write a corrected equation for RF in terms of SCO, DCO, and NCO meioses. l. Using your answer to part (g), rewrite the corrected RF equation from part (k) in terms of the numbersof the various tetrad types.
m. The equation you just wrote in part (l) is a corrected equation for RF that takes into account doublecrossovers that would otherwise have been missed. Use this improved formula to calculate a moreaccurate distance between the his and lys genes than the one you calculated in part (c).

Answers: 3


Other questions on the subject: Biology

Biology, 22.06.2019 02:00, Bashirar19
The united states produces an average of 429 billion pounds of food annually. about 133 billion pounds of that food ends up as waste. the percentage of food that the united states wastes each year is %.
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 08:00, suhailalitariq
Which feature of a human community is similar to a niche in a biological community
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 08:30, tabathahasaunicorn1
Which macromolecule catalyzes chemical reactions this be considered enzyme chemical reactions thus he considering enzymes
Answers: 3

Biology, 22.06.2019 09:00, zhellyyyyy
Group control group #1 experimental group yes yes yes control group #2 no new drug orange juice bed rest no yes no yes ves which of the following is the best explanation of why a second control group was included in this experiment? o a. to provide the volunteers in the study with something to drink o b. to prove that the common cold cannot be cured c. to confuse anyone who is trying to steal their new drug and sell it as their own invention o d. to researchers conclude that results are related to the new drug and not to the orange juice submit e previous
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
This problem leads you through the derivation of a corrected equation for RF in yeast tetrad analysi...
Questions in other subjects:

History, 17.12.2021 06:00



Mathematics, 17.12.2021 06:00

Mathematics, 17.12.2021 06:00


English, 17.12.2021 06:00


Mathematics, 17.12.2021 06:00

Mathematics, 17.12.2021 06:00



