Biology, 26.02.2020 03:58 antonio9768
You study color variants of Arabidopsis hypotheticus, a plant with red flowers. You have obtained three pure-breeding mutant lines, all named for their place of origin. Two lines have white flowers (Aberdeen White and Victoria White), and one has yellow flowers (Kansas Yellow).
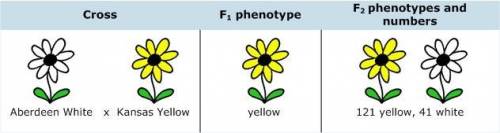
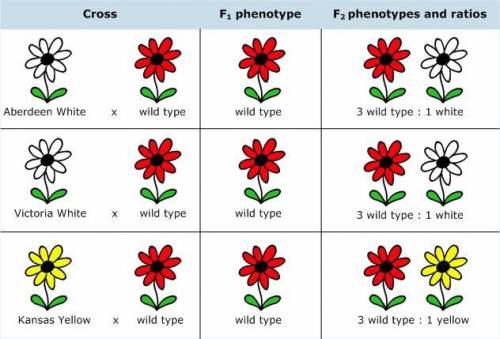
You begin your analysis by crossing each line with wild-type plants and selfing the F1 to produce an F2 generation.[Crosses between Aberdeen White and wild type, Victoria White and wild type, and Kansas Yellow and wild type] From these crosses you conclude that the mutations in all three lines are recessive to the wild type.
Crossing lines with the same recessive phenotype
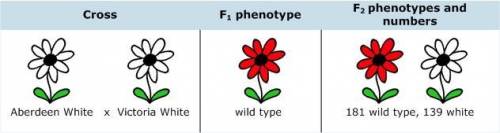
You continue your analysis by crossing the Aberdeen White and Victoria White lines. This time you count the actual numbers of progeny in the two F2 phenotypic classes.
[Cross between Aberdeen White and Victoria White]
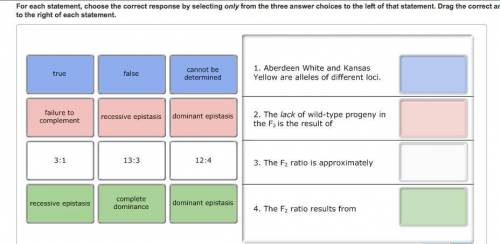
You also self several wild-type plants from the F2 and determine that some of them are pure-breeding. What can you conclude from these results?

Answers: 1


Other questions on the subject: Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 18:00, jstephanie644
Cells tend to have a relatively small and uniform size. why aren’t cells larger?
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 05:30, sandygarcia65
“in 1492 columbus sailed the ocean blue” is an example of: a)explicit memory b) procedural memory c) semantic memory d)episodic memory
Answers: 3

Biology, 22.06.2019 09:00, chloeann4688
Which of these is not a nucleotide base found in dna?
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 16:30, debnkids691
In what ways does the study of human population differ from the study of wildlife ecology
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
You study color variants of Arabidopsis hypotheticus, a plant with red flowers. You have obtained th...
Questions in other subjects:



History, 17.07.2019 08:30


English, 17.07.2019 08:30




Social Studies, 17.07.2019 08:30